|
|
The Australian Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications
ISSN 1449-5910 |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Paper's Title:
Optimization and Approximation for Polyhedra in Separable Hilbert Spaces
Author(s):
Paolo d'Alessandro
Department of Mathematics,
Third University of Rome,
Italy.
E-mail: pdalex45@gmail.com
Abstract:
This paper studies infinite dimensional polyhedra, covering the case in which range spaces of operators defining inequality systems are not closed. A rangespace method of linear programming is generalized to infinite dimensions and finite dimensional methods of approximation are introduced.
Paper's Title:
Generalizing Polyhedra to Infinite Dimension
Author(s):
Paolo d'Alessandro
Department of Mathematics, Third University of Rome,
Lgo S.L. Murialdo 1, 00146 Rome, Italy.
URL:
http://www.mat.uniroma3.it/users/dalex/dalex.html.
Abstract:
This paper generalizes polyhedra to infinite dimensional Hilbert spaces as countable intersections of closed semispaces. Highlights are the structure theory that shows that a polyhedron is the sum of compact set (in a suitable topology) plus a closed pointed cone plus a closed subspace, giving the internal representation of polyhedra. In the final part the dual range space technique is extended to the solution of infinite dimensional LP problems.
Paper's Title:
Ellipses Inscribed in Parallelograms
Author(s):
A. Horwitz
Penn State University,
25 Yearsley Mill Rd.
Media, PA 19063
U. S. A.
alh4@psu.edu
Abstract:
We prove that there exists a unique ellipse of minimal eccentricity, EI, inscribed in a parallelogram, Ð. We also prove that the smallest nonnegative angle between equal conjugate diameters of $EI equals the smallest nonnegative angle between the diagonals of Ð. We also prove that if EM is the unique ellipse inscribed in a rectangle, R, which is tangent at the midpoints of the sides of R, then EM is the unique ellipse of minimal eccentricity, maximal area, and maximal arc length inscribed in R. Let Ð be any convex quadrilateral. In previous papers, the author proved that there is a unique ellipse of minimal eccentricity, EI, inscribed in Ð, and a unique ellipse, EO, of minimal eccentricity circumscribed about Ð. We defined Ð to be bielliptic if EI and EO have the same eccentricity. In this paper we show that a parallelogram, Ð, is bielliptic if and only if the square of the length of one of the diagonals of Ð equals twice the square of the length of one of the sides of Ð .
Paper's Title:
Ellipses of Maximal Area and of Minimal Eccentricity Inscribed in a Convex Quadrilateral
Author(s):
Alan Horwitz
Penn State University,
25 Yearsley Mill Rd., Media, Pa 19063
alh4@psu.edu
Url: www.math.psu.edu/horwitz
Abstract:
Let Ð be a convex quadrilateral in the plane and let M1 and M2 be the midpoints
of the diagonals of Ð. It is well–known that if E is an ellipse inscribed in Ð, then the center of
E must lie on Z, the open line segment connecting M1 and M2 . We use a theorem of Marden
relating the foci of an ellipse tangent to the lines thru the sides of a triangle and the zeros of a
partial fraction expansion to prove the converse: If P lies on Z, then there is a unique ellipse with
center P inscribed in Ð. This completely characterizes the locus of centers of ellipses inscribed
in Ð. We also show that there is a unique ellipse of maximal area inscribed in Ð. Finally, we
prove our most signifigant results: There is a unique ellipse of minimal eccentricity inscribed in
Ð.
Paper's Title:
Differential Equations for Indicatrices, Spacelike and Timelike Curves
Author(s):
Sameer, Pradeep Kumar Pandey
Department of Mathematics,
Jaypee University of Information Technology,
Solan, Himachal Pradesh,
India.
E-mail: sksameer08@gmail.com,
pandeypkdelhi@gmail.com
Abstract:
Motivated by the recent work of Deshmukh et al. [20], in this paper we show that Tangent, Binormal, and Principal Normal indicatrices do not form non-trivial differential equations. Finally, we obtain the 4th-order differential equations for spacelike and timelike curves.
Paper's Title:
Viability
Theory And Differential Lanchester Type Models For Combat.
Differential Systems.
Author(s):
G. Isac and A. Gosselin
Department Of
Mathematics, Royal Military College Of Canada,
P.O. Box 17000, Stn Forces, Kingston,
Ontario, Canada K7k 7b4
isac-g@rmc.ca
gosselin-a@rmc.ca
URL:
http://www.rmc.ca/academic/math_cs/isac/index_e.html
URL:
http://www.rmc.ca/academic/math_cs/gosselin/index_e.html
Abstract:
In 1914, F.W. Lanchester proposed several mathematical models based on differential equations to describe combat situations [34]. Since then, his work has been extensively modified to represent a variety of competitions including entire wars. Differential Lanchester type models have been studied from many angles by many authors in hundreds of papers and reports. Lanchester type models are used in the planning of optimal strategies, supply and tactics. In this paper, we will show how these models can be studied from a viability theory stand point. We will introduce the notion of winning cone and show that it is a viable cone for these models. In the last part of our paper we will use the viability theory of differential equations to study Lanchester type models from the optimal theory point of view.
Paper's Title:
Shape Diagrams for 2D Compact Sets - Part I: Analytic
Convex Sets.
Author(s):
S. Rivollier, J. Debayle and J.-C. Pinoli
Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Mines de Saint-Etienne,
CIS - LPMG, UMR CNRS 5148, 158 cours Fauriel,
42023 Saint-Etienne Cedex 2, France.
rivollier@emse.fr;
debayle@emse.fr; pinoli@emse.fr
Abstract:
Shape diagrams are representations in the Euclidean plane introduced to study 3-dimensional and 2-dimensional compact convex sets. Such a set is represented by a point within a shape diagram whose coordinates are morphometrical functionals defined as normalized ratios of geometrical functionals. Classically, the geometrical functionals are the area, the perimeter, the radii of the inscribed and circumscribed circles, and the minimum and maximum Feret diameters. They allow thirty-one shape diagrams to be built. Most of these shape diagrams can also been applied to more general compact sets than compact convex sets. Starting from these six classical geometrical functionals, a detailed comparative study has been performed in order to analyze the representation relevance and discrimination power of these thirty-one shape diagrams. The purpose of this paper is to present the first part of this study, by focusing on analytic compact convex sets. A set will be called analytic if its boundary is piecewise defined by explicit functions in such a way that the six geometrical functionals can be straightforwardly calculated. The second and third part of the comparative study are published in two following papers [19.20]. They are focused on analytic simply connected sets and convexity discrimination for analytic and discretized simply connected sets, respectively.
Paper's Title:
Global Analysis on Riemannian Manifolds
Author(s):
Louis Omenyi and Michael Uchenna
Department of Mathematics, Computer
Science, Statistics and Informatics,
Alex Ekwueme Federal University, Ndufu-Alike,
Nigeria.
E-mail: omenyi.louis@funai.edu.ng,
michael.uchenna@funai.edu.ng
URL: http://www.funai.edu.ng
Abstract:
In this paper, an exposition of the central concept of global analysis on a Riemannan manifold is given. We extend the theory of smooth vector fields from open subsets of Euclidean space to Riemannan manifolds. Specifically, we prove that a Riemannian manifold admits a unique solution for a system of ordinary differential equations generated by the flow of smooth tangent vectors. The idea of partial differential equations on Riemannian manifold is highlighted on the unit sphere.
Paper's Title:
Optimization Techniques on Affine Differential Manifolds
Author(s):
Ali S Rasheed, Faik Mayah and Ahmed A H AL-Jumaili
Ministry of Higher Education and
Scientific Research,
Iraq.
E-mail: ahmedhashem@gmail.com
Department of Physics, College of
Sciences,
University of Wasit,
Iraq.
E-mail: faik.mayah@gmail.com
Abstract:
In addition to solid ground of Riemannian manifolds fundamentals, this article interviews some popular optimization methods on Riemannian manifolds. Several optimization problems can be better stated on manifolds rather than Euclidean space, such as interior point methods, which in turns based on self-concordant functions (logarithmic barrier functions). Optimization schemes like the steepest descent scheme, the Newton scheme, and others can be extended to Riemannian manifolds. This paper introduces some Riemannian and non-Riemannian schemes on manifolds.
Paper's Title:
Error Bounds for Numerical Integration of Functions of Lower Smoothness and Gauss-Legendre Quadrature Rule
Author(s):
Samuel A. Surulere and Abiola O. Oladeji
Tshwane University of Technology
Department of Mathematics and Statistics
175, Nelson Mandela drive, Arcadia, Pretoria,
South Africa.
E-mail: samuel.abayomi.sas@gmail.com
Abstract:
The error bounds of the rectangular, trapezoidal and Simpson's rules which are commonly used in approximating the integral of a function (f(x)) over an interval ([a,b]) were estimated. The error bounds of the second, and third generating functions of the Gauss-Legendre quadrature rules were also estimated in this paper. It was shown that for an (f(t)) whose smoothness is increasing, the accuracy of the fourth, sixth and eighth error bound of the second, and third generating functions of the Gauss-Legendre quadrature rule does not increase. It was also shown that the accuracy of the fourth error bound of the Simpson's (1/3) and (3/8) rules does not increase.
Paper's Title:
Oscillations of First Order Linear Delay Difference Equations
Author(s):
G. E. Chatzarakis and I. P. Stavroulakis
Department of Mathematics, University of Ioannina,
451 10, Greece
ipstav@cc.uoi.gr
Abstract:
Consider the first order linear delay difference equation of
the form ![]()
![]() where
where
![]() is
a sequence of nonnegative real numbers, k is a positive integer and
is
a sequence of nonnegative real numbers, k is a positive integer and ![]() denotes
the forward difference operator
denotes
the forward difference operator ![]() New
oscillation criteria are established when the well-known oscillation conditions
New
oscillation criteria are established when the well-known oscillation conditions
![]() and
and
![]() are
not satisfied. The results obtained essentially improve known results in the
literature.
are
not satisfied. The results obtained essentially improve known results in the
literature.
Paper's Title:
Integer Sums of Powers of Trigonometric Functions (MOD p), for prime p
Author(s):
G. J. Tee
Department of Mathematics, University of Auckland,
Auckland,
New Zealand
tee@math.auckland.ac.nz
Abstract:
Many multi--parameter families of congruences (mod p) are found for integer
sums of
qth powers of the trigonometric functions over various sets of equidistant
arguments, where
p is any prime factor of q. Those congruences provide sensitive
tests for the accuracy
of software for evaluating trigonometric functions to high precision.
Paper's Title:
Some Homogeneous Cyclic Inequalities of Three Variables of Degree Three and Four
Author(s):
TETSUYA ANDO
Department of Mathematics and Informatics,
Chiba University, Chiba 263-8522, JAPAN
ando@math.s.chiba-u.ac.jp
Abstract:
We shall show that the three variable cubic inequality
t2 (a3+b3+c3) + (t4-2t)(ab2+bc2+ca2)
≥ (2t3-1)(a2b+b2c+c2a)
+ (3t4-6t3+3t2-6t+3)abc
holds for non-negative a, b, c, and for any real number t.
We also show some similar three variable cyclic quartic inequalities.
Paper's Title:
Inequalities for Discrete F-Divergence Measures: A Survey of Recent Results
Author(s):
Sever S. Dragomir1,2
1Mathematics, School of Engineering
& Science
Victoria University, PO Box 14428
Melbourne City, MC 8001,
Australia
E-mail: sever.dragomir@vu.edu.au
2DST-NRF Centre of Excellence in the Mathematical and Statistical Sciences,
School of Computer Science & Applied Mathematics,
University of the Witwatersrand,
Private Bag 3, Johannesburg 2050,
South Africa
URL:
http://rgmia.org/dragomir
Abstract:
In this paper we survey some recent results obtained by the author in providing various bounds for the celebrated f-divergence measure for various classes of functions f. Several techniques including inequalities of Jensen and Slater types for convex functions are employed. Bounds in terms of Kullback-Leibler Distance, Hellinger Discrimination and Varation distance are provided. Approximations of the f-divergence measure by the use of the celebrated Ostrowski and Trapezoid inequalities are obtained. More accurate approximation formulae that make use of Taylor's expansion with integral remainder are also surveyed. A comprehensive list of recent papers by several authors related this important concept in information theory is also included as an appendix to the main text.
Paper's Title:
Semivectorial Bilevel Optimization on Affine-Finsler-Metric Manifolds
Author(s):
Faik Mayah1, Ali S Rasheed2 and Naseif J. Al- Jawari3
1Department of Physics,
College of Sciences,
University of Wasit,
Iraq.
E-mail: faik.mayah@gmail.com
2Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research,
Iraq.
E-mail: ali.math2018@yahoo.com
ahmedhashem@gmail.com
3Dept.
of Mathematics,
College of Science,
Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad,
Iraq.
E-mail: nsaif642014@yahoo.com
Abstract:
A Finsler manifold is a differential manifold together with a Finsler metric, in this paper we construct a new class of Finsler metric affine manifolds on bilevel semivectorial with optimization problems. The first steps for this purpose involve the study of bilevel optimization on affine manifolds. The bilevel programming problem can be viewed as a static version of the noncooperative, two-person game which was introduced in the context of unbalanced economic markets. Bilevel optimization is a special kind of optimization where one problem is embedded within another.
Paper's Title:
Ellipses of Minimal Area and of Minimal Eccentricity Circumscribed About a Convex Quadrilateral
Author(s):
Alan Horwitz
Penn State University,
25 Yearsley Mill Rd.,
Media, PA 19063,
U.S.A
alh4@psu.edu
Abstract:
First, we fill in key gaps in Steiner's nice characterization of
the most nearly circular ellipse which passes through the vertices of a convex
quadrilateral,
![]() . Steiner proved that there is only one pair of conjugate
directions, M1 and M2, that belong to all ellipses of circumscription.
Then he proves that if there is an ellipse, E, whose equal
conjugate diameters possess the directional constants M1 and M2,
then E must be an ellipse of circumscription which has minimal eccentricity.
However, Steiner does not show the existence or uniqueness of such an ellipse.
We prove that there is a unique ellipse of minimal eccentricity which passes
through the vertices of
. Steiner proved that there is only one pair of conjugate
directions, M1 and M2, that belong to all ellipses of circumscription.
Then he proves that if there is an ellipse, E, whose equal
conjugate diameters possess the directional constants M1 and M2,
then E must be an ellipse of circumscription which has minimal eccentricity.
However, Steiner does not show the existence or uniqueness of such an ellipse.
We prove that there is a unique ellipse of minimal eccentricity which passes
through the vertices of
![]() . We also show that there exists an ellipse which passes through the vertices of
. We also show that there exists an ellipse which passes through the vertices of
![]() and whose
equal conjugate diameters
possess the directional constants M1 and M2. We also show
that there exists a unique ellipse of minimal area which passes through the
vertices of
and whose
equal conjugate diameters
possess the directional constants M1 and M2. We also show
that there exists a unique ellipse of minimal area which passes through the
vertices of
![]() . Finally, we call a convex quadrilateral,
. Finally, we call a convex quadrilateral,
![]() , bielliptic if the unique
inscribed and circumscribed ellipses of minimal eccentricity have the same
eccentricity. This generalizes the notion of bicentric quadrilaterals. In
particular, we show the existence of a bielliptic convex quadrilateral which is
not bicentric.
, bielliptic if the unique
inscribed and circumscribed ellipses of minimal eccentricity have the same
eccentricity. This generalizes the notion of bicentric quadrilaterals. In
particular, we show the existence of a bielliptic convex quadrilateral which is
not bicentric.
Paper's Title:
Two Geometric Constants Related to Isosceles Orthogonality on Banach Space
Author(s):
Huayou Xie, Qi Liu and Yongjin Li
Department of Mathematics,
Sun Yat-sen University,
Guangzhou, 510275,
P. R. China.
E-mail: xiehy33@mail2.sysu.edu.cn
Department of Mathematics,
Sun Yat-sen University,
Guangzhou, 510275,
P. R. China.
E-mail: liuq325@mail2.sysu.edu.cn
Department of Mathematics,
Sun Yat-sen University,
Guangzhou, 510275,
P. R. China.
E-mail: stslyj@mail.sysu.edu.cn
Abstract:
In this paper, we introduce new geometric constant C(X,ai,bi,ci,2) to measure the difference between isosceles orthogonality and special Carlsson orthogonalities. At the same time, we also present the geometric constant C(X,ai,bi,ci), which is a generalization of the rectangular constant proposed by Joly. According to the inequality on isosceles orthogonality, we give the boundary characterization of these geometric constants. Then the relationship between these geometric constants and uniformly non-square property can also be discussed. Furthermore, we show that there is a close relationship between these geometric constants and some important geometric constants.
Paper's Title:
On the Equiform Geometry of the Involute-evolute Curve Couple in Hyperbolic and de Sitter Spaces
Author(s):
M. Khalifa Saad, H. S. Abdel-Aziz and A. A. Abdel-Salam
Department of Mathematics,
Faculty of Science,
Islamic University of Madinah,
KSA.
E-mail: mohammed.khalifa@iu.edu.sa
Department of Mathematics,
Faculty of Science,
Sohag University, Sohag,
EGYPT.
E-mail: habdelaziz2005@yahoo.com
Department of Mathematics,
Faculty of Science,
Sohag University, Sohag,
EGYPT.
E-mail: asem2e@yahoo.com
Abstract:
In this paper, we aim to investigate the equiform differential geometric properties of the involute-evolute curve couple with constant equiform curvatures in three-dimensional hyperbolic and de Sitter spaces. Also, we obtain some relations between the curvature functions of these curves and investigate some special curves with respect to their equiform curvatures. Finally, we defray two computational examples to support our main findings.
Paper's Title:
Multilinear Fractional Integral Operators on Herz Spaces
Author(s):
Yasuo Komori-Furuya
School of High Technology and Human Welfare,
Tokai University,
317 Nishino Numazu Shizuoka, 410-0395
Japan
Abstract:
We prove the boundedness of the multilinear fractional integral operators of Kenig and Stein type on Herz spaces. We also show that our results are optimal.
Paper's Title:
Polyanalytic Functions on Subsets of Z[i]
Author(s):
Abtin Daghighi
Linköping University,
SE-581 83,
Sweden.
E-mail: abtindaghighi@gmail.com
Abstract:
For positive integers q we consider the kernel of the powers Lq where L is one of three kinds of discrete analogues of the Cauchy-Riemann operator. The first two kinds are well-studied, but the third kind less so. We give motivations for further study of the third kind especially since its symmetry makes it more appealing for the cases q≥ 2.
From an algebraic perspective it makes sense that the chosen multiplication on the kernels is compatible with the choice of pseudo-powers. We propose such multiplications together with associated pseudo-powers. We develop a proof-tool in terms of certain sets of uniqueness.
Paper's Title:
Simplicial (co)-homology of Band Semigroup
Author(s):
Yasser Farhat
Academic Support Department,
Abu Dhabi Polytechnic,
P.O. Box 111499, Abu Dhabi,
UAE.
E-mail: yasser.farhat@adpoly.ac.ae, farhat.yasser.1@gmail.com
Abstract:
We consider the Banach algebra l1(S), with convolution, where S is a band semigroup. We prove directly, without using the cyclic cohomology, that the simplicial cohomology groups Hn(l1(S), l1(S)*) vanish for all n≥1. This proceeds in three steps. In each step, we introduce a bounded linear map. By iteration in each step, we achieve our goal.
Paper's Title:
Sweeping Surfaces with Darboux Frame in Euclidean 3-space E3
Author(s):
F. Mofarreh, R. Abdel-Baky and N. Alluhaibi
Mathematical Science Department, Faculty
of Science,
Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University
Riyadh 11546,
Saudi Arabia.
E-mail: fyalmofarrah@pnu.edu.sa
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science,
University of Assiut,
Assiut 71516,
Egypt.
E-mail: rbaky@live.com
Department of Mathematics Science and
Arts, College Rabigh Campus,
King Abdulaziz University
Jeddah,
Saudi Arabia.
E-mail: nallehaibi@kau.edu.sa
Abstract:
The curve on a regular surface has a moving frame and it is called Darboux frame. We introduce sweeping surfaces along the curve relating to the this frame and investigate their geometrical properties. Moreover, we obtain the necessary and sufficient conditions for these surfaces to be developable ruled surfaces. Finally, an example to illustrate the application of the results is introduced.
Paper's Title:
Equilibria and Periodic Solutions of Projected Dynamical Systems on Sets with Corners
Author(s):
Matthew D. Johnston and Monica-Gabriela Cojocaru
Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Waterloo,
Ontario, Canada
mdjohnst@math.uwaterloo.ca
Department of Mathematics & Statistics, University of
Guelph,
Ontario, Canada
mcojocar@uoguelph.ca
Abstract:
Projected dynamical systems theory represents a bridge between the
static worlds of variational inequalities and equilibrium
problems, and the dynamic world of ordinary differential
equations. A projected dynamical system (PDS) is given by the flow
of a projected differential equation, an ordinary differential
equation whose trajectories are restricted to a constraint set
K. Projected differential equations are defined by discontinuous
vector fields and so standard differential equations theory cannot
apply. The formal study of PDS began in the 90's, although some
results existed in the literature since the 70's. In this paper we
present a novel result regarding existence of equilibria and
periodic cycles of a finite dimensional PDS on constraint sets
K, whose points satisfy a corner condition. The novelty is due
to proving existence of boundary equilibria without using a
variational inequality approach or monotonicity type conditions.
Paper's Title:
Contact With Adhesion between a Deformable Body and a Foundation
Author(s):
B. Teniou and M. Sofonea
Laboratoire de Mathematiques Appliquées et Modélisation,
Université Mentouri, Constantine 25000,
Algeria
tenioubou2@yahoo.fr
Laboratoire de Mathématiques et Physiques pour les Systémes,
Univesité de Perpignan,
France.
sofonea@univ-perp.fr
Abstract:
The aim of this work is study a dynamic contact problem between a
deformable body and a foundation where the deformations are supposed
to be small. The contact is with adhesion and normal compliance. The
behavior of this body is modeled by a nonlinear
elastic-visco-plastic law. The evolution of bonding field is
described by a nonlinear differential equation. We derive a
variational formulation of the contact problem and we prove the
existence and uniqueness of its solution. The proof is based on the
construction of three intermediate problems and then we construct a
contraction mapping whose unique fixed point will be the weak
solution of the mechanical problem.
Paper's Title:
Purely Unrectifiable Sets with Large Projections
Author(s):
Harold R. Parks
Department of Mathematics,
Oregon State University,
Corvallis, Oregon 97331--4605,
USA
parks@math.oregonstate.edu
URL: http://www.math.oregonstate.edu/people/view/parks/
Abstract:
For n≥2,
we give a construction of a compact
subset of ![]() that is dispersed enough that it is
purely unrectifiable, but that nonetheless
has an orthogonal projection that hits every
point of an (n-1)-dimensional unit cube.
Moreover, this subset has the additional
surprising property that
the orthogonal projection onto
any straight line in
that is dispersed enough that it is
purely unrectifiable, but that nonetheless
has an orthogonal projection that hits every
point of an (n-1)-dimensional unit cube.
Moreover, this subset has the additional
surprising property that
the orthogonal projection onto
any straight line in
![]() is a set of positive
1-dimensional Hausdorff measure.
is a set of positive
1-dimensional Hausdorff measure.
Paper's Title:
A Low Order Least-Squares Nonconforming Finite Element Method for Steady Magnetohydrodynamic Equations
Author(s):
Z. Yu, D. Shi and H. Zhu
College of Science,
Zhongyuan
University of Technology,
Zhengzhou 450007,
China.
E-mail:
5772@zut.edu.cn
School of Mathematics and Statistics,
Zhengzhou University,
Zhengzhou 450001,
China.
E-mail:
shi_dy@126.com
Mathematics Department,
University of Southern Mississippi,
Hattiesburg MS, 39406,
U.S.A
E-mail:
huiqing.zhu@usm.edu
Abstract:
A low order least-squares nonconforming finite element (NFE) method is proposed for magnetohydrodynamic equations with EQ1rot element and zero-order Raviart-Thomas element. Based on the above element's typical interpolations properties, the existence and uniqueness of the approximate solutions are proved and the optimal order error estimates for the corresponding variables are derived.
Paper's Title:
Solving Two Point Boundary Value Problems by Modified Sumudu Transform Homotopy Perturbation Method
Author(s):
Asem AL Nemrat and Zarita Zainuddin
School of Mathematical Sciences,
Universiti Sains Malaysia,
11800 Penang,
Malaysia.
E-mail: alnemrata@yahoo.com
zarita@usm.my
Abstract:
This paper considers a combined form of the Sumudu transform with the modified homotopy perturbation method (MHPM) to find approximate and analytical solutions for nonlinear two point boundary value problems. This method is called the modified Sumudu transform homotopy perturbation method (MSTHPM). The suggested technique avoids the round-off errors and finds the solution without any restrictive assumptions or discretization. We will introduce an appropriate initial approximation and furthermore, the residual error will be canceled in some points of the interval (RECP). Only a first order approximation of MSTHPM will be required, as compared to STHPM, which needs more iterations for the same cases of study. After comparing figures between approximate, MSTHPM, STHPM and numerical solutions, it is found through the solutions we have obtained that they are highly accurate, indicating that the MSTHPM is very effective, simple and can be used to solve other types of nonlinear boundary value problems (BVPs).
Paper's Title:
Constraint Qualifications for Multiobjective Programming Problems on Hadamard Manifolds
Author(s):
Arnav Ghosh, Balendu Bhooshan Upadhyay and I.M. Stancu-Minasian
Department of Mathematics,
Indian Institute of Technology Patna,
Patna,
India.
E-mail: arnav_2021ma09@iitp.ac.in
Department of Mathematics,
Indian Institute of Technology Patna,
Patna,
India.
E-mail: bhooshan@iitp.ac.in
"Gheorghe Mihoc-Caius Iacob" Institute of
Mathematical Statistics and Applied Mathematics of the Romanian Academy,
Bucharest,
Romania.
E-mail: stancu_minasian@yahoo.com
Abstract:
The study of optimization methods on manifolds has emerged as an immensely significant topic in mathematics due its ubiquitous applicability as well as various computational advantages associated with it. Motivated by this fact, the present article is devoted to the study of a class of constrained multiobjective programming problems (MOPP) in the framework of Hadamard manifolds. We present the generalized Guignard constraint qualification (GGCQ) in the framework of Hadamard manifolds for (MOPP). Employing (GGCQ), we derive Karush-Kuhn-Tucker type necessary optimality criteria for (MOPP). Moreover, we present several other constraint qualifications (CQs) on Hadamard manifolds, namely, Abadie's CQ, generalized Abadie's CQ, Cottle-type CQ, Slater-type CQ, linear CQ, linear objective CQ and Mangasarian-Fromovitz CQ. Further, we establish various relations between these constraint qualifications. In particular, we show that these constraint qualifications, in turn, become sufficient conditions ensuring that (GGCQ) is satisfied.
Paper's Title:
On a Generalized Biharmonic Equation in Plane Polars with Applications to Functionally Graded Materials
Author(s):
Ciro D'Apice
Department of Information Engineering and Applied Mathematics (DIIMA),
University of Salerno, 84084 Fisciano (SA),
Salerno, Italy.
dapice@diima.unisa.it
Abstract:
In this paper we consider a generalized biharmonic
equation modelling a two-dimensional inhomogeneous
elastic state in the curvilinear rectangle ![]()
![]() where
where ![]() denote plane polar
coordinates. Such an arch--like region is maintained in equilibrium under
self--equilibrated traction applied on the edge
denote plane polar
coordinates. Such an arch--like region is maintained in equilibrium under
self--equilibrated traction applied on the edge ![]() while the other three
edges
while the other three
edges ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are traction free. Our
aim is to derive some explicit spatial exponential decay bounds for the
specific Airy stress function and its derivatives. Two types of smoothly
varying inhomogeneity are considered: (i) the elastic moduli vary
smoothly with the polar angle, (ii) they vary smoothly
with the polar distance. Such types of smoothly varying inhomogeneous elastic
materials provide a model for technological important functionally graded
materials. The results of the present paper prove how the spatial decay rate
varies with the constitutive profile.
are traction free. Our
aim is to derive some explicit spatial exponential decay bounds for the
specific Airy stress function and its derivatives. Two types of smoothly
varying inhomogeneity are considered: (i) the elastic moduli vary
smoothly with the polar angle, (ii) they vary smoothly
with the polar distance. Such types of smoothly varying inhomogeneous elastic
materials provide a model for technological important functionally graded
materials. The results of the present paper prove how the spatial decay rate
varies with the constitutive profile.
Paper's Title:
An Improvement of the Hermite-Hadamard Inequality for Functions Convex on the Coordinates
Author(s):
Milica Klaričić Bakula
Faculty of Science,
University of Split,
Teslina 12, 21000 Split.
Croatia
E-mail: milica@pmfst.hr
Abstract:
An improvement of the Hermite-Hadamard inequality for functions convex on the coordinates is given.
Paper's Title:
Ostrowski Type Inequalities for Lebesgue Integral: a Survey of Recent Results
Author(s):
Sever S. Dragomir1,2
1Mathematics, School of Engineering
& Science
Victoria University, PO Box 14428
Melbourne City, MC 8001,
Australia
E-mail: sever.dragomir@vu.edu.au
2DST-NRF Centre of Excellence in the Mathematical and Statistical Sciences,
School of Computer Science & Applied Mathematics,
University of the Witwatersrand,
Private Bag 3, Johannesburg 2050,
South Africa
URL:
http://rgmia.org/dragomir
Abstract:
The main aim of this survey is to present recent results concerning Ostrowski type inequalities for the Lebesgue integral of various classes of complex and real-valued functions. The survey is intended for use by both researchers in various fields of Classical and Modern Analysis and Mathematical Inequalities and their Applications, domains which have grown exponentially in the last decade, as well as by postgraduate students and scientists applying inequalities in their specific areas.
Paper's Title:
Mapped Chebyshev Spectral Methods for Solving Second Kind Integral Equations on the Real Line
Author(s):
Ahmed Guechi and Azedine Rahmoune
Department of Mathematics, University of Bordj Bou Arréridj,
El Anasser, 34030, BBA,
Algeria.
E-mail: a.guechi2017@gmail.com
E-mail: a.rahmoune@univ-bba.dz
Abstract:
In this paper we investigate the utility of mappings to solve numerically an important class of integral equations on the real line. The main idea is to map the infinite interval to a finite one and use Chebyshev spectral-collocation method to solve the mapped integral equation in the finite interval. Numerical examples are presented to illustrate the accuracy of the method.
Paper's Title:
Analysis of a Frictional Contact Problem for Viscoelastic Piezoelectric Materials
Author(s):
Meziane Said Ameur, Tedjani Hadj Ammar and Laid Maiza
Departement of Mathematics,
El Oued University,
P.O. Box 789, 39000 El Oued,
Algeria.
E-mail:
said-ameur-meziane@univ-eloued.dz
Departement of Mathematics,
El Oued University,
P.O. Box 789, 39000 El Oued,
Algeria.
E-mail:
hadjammar-tedjani@univ-eloued.dz
Department of Mathematics,
Kasdi Merbah University,
30000 Ouargla,
Algeria.
E-mail: maiza.laid@univ-ouargla.dz
Abstract:
In this paper, we consider a mathematical model that describes the quasi-static process of contact between two thermo-electro-viscoelastic bodies with damage and adhesion. The damage of the materials caused by elastic deformations. The contact is frictional and modeled with a normal compliance condition involving adhesion effect of contact surfaces. Evolution of the bonding field is described by a first order differential equation. We derive variational formulation for the model and prove an existence and uniqueness result of the weak solution. The proof is based on arguments of evolutionary variational inequalities, parabolic inequalities, differential equations, and fixed point theorem.
Paper's Title:
On Ruled Surfaces According to Quasi-Frame in Euclidean 3-Space
Author(s):
M. Khalifa Saad and R. A. Abdel-Baky
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of
Science,
Islamic University of Madinah,
KSA.
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science,
Sohag University, Sohag,
EGYPT.
E-mail:
mohamed_khalifa77@science.sohag.edu.eg,
mohammed.khalifa@iu.edu.sa
Department of Mathematics, Faculty of
Science,
Assiut University, Assiut,
EGYPT.
E-mail: rbaky@live.com
Abstract:
This paper aims to study the skew ruled surfaces by using the quasi-frame of Smarandache curves in the Euclidean 3-space. Also, we reveal the relationship between Serret-Frenet and quasi-frames and give a parametric representation of a directional ruled surface using the quasi-frame. Besides, some comparative examples are given and plotted which support our method and main results.
Paper's Title:
Analysis of a Dynamic Elasto-viscoplastic Frictionless Antiplan Contact Problem with Normal Compliance
Author(s):
A. Ourahmoun1, B. Bouderah2, T. Serrar3
1,2Applied Mathematics
Laboratory,
M'sila University, 28000,
Algeria.
E-mail: ourahmounabbes@yahoo.fr
3Applied Mathematics
Laboratory,
Setif 1 University, 19000,
Algeria.
Abstract:
We consider a mathematical model which describes the dynamic evolution of a thermo elasto viscoplastic contact problem between a body and a rigid foundation. The mechanical and thermal properties of the obstacle coating material near its surface. A variational formulation of this dynamic contact phenomenon is derived in the context of general models of thermo elasto viscoplastic materials. The displacements and temperatures of the bodies in contact are governed by the coupled system consisting of a variational inequality and a parabolic differential equation. The proof is based on a classical existence and uniqueness result on parabolic inequalities,differential equations and fixed point arguments.
Paper's Title:
Timelike Surfaces with a Common Line of Curvature in Minkowski 3-Space
Author(s):
M.K. Saad, A.Z. Ansari, M. Akram and F. Alharbi
Department of Mathematics ,
Faculty of Science,
Islamic University of Madinah,
KSA
Abstract:
In this paper, we analyze the problem of constructing a timelike surface family from a given non-null curve line of curvature. Using the Frenet frame of the non-null curve in Minkowski space E13 we express the family of surfaces as a linear combination of the components of this frame, and derive the necessary and sufficient conditions for the coefficients to satisfy both the line of curvature and the isoparametric requirements. In addition, a necessary and sufficient condition for the given non-null curve to satisfy the line of curvature and the geodesic requirements is investigated. The extension to timelike surfaces of revolution is also outlined. Meanwhile, some representative non-null curves are chosen to construct the corresponding timelike surfaces which possessing these curves as lines of curvature. Results presented in this paper have applications in geometric modeling and the manufacturing of products. In addition, some computational examples are given and plotted.
Paper's Title:
Corrigendum for Differential Equations for Indicatrices, Spacelike and Timelike Curves
Author(s):
Sameer, Pradeep Kumar Pandey
Department of Mathematics,
Jaypee University of Information Technology,
Solan, Himachal Pradesh,
India.
E-mail: sksameer08@gmail.com,
pandeypkdelhi@gmail.com
ABSTRACT NOT FOUND. WEBSITE ERROR
Abstract:
Paper's Title:
New Coincidence and Fixed Point Theorems for Strictly Contractive Hybrid Maps
Author(s):
S. L. Singh and Amal M. Hashim
21, Govind Nagar, Rishikesh 249201,
Ua, India
vedicmri@sancharnet.in
Dept. of Math., College of Science,
Univ. of Basarah,
Iraq.
Abstract:
The purpose of this paper is to study the (EA)-property and noncompatible maps
of a hybrid pair of single-valued and multivalued maps in fixed point considerations. Such maps
have the remarkable property that they need not be continuous at their common fixed points. We
use this property to obtain some coincidence and fixed point theorems for strictly contractive
hybrid maps without using their continuity and completeness or compactness of the space.
Paper's Title:
Approximation of Common Fixed Points of a Finite Family of Asymptotically Demicontractive Mappings in Banach Spaces
Author(s):
Yuchao Tang, Yong Cai, Liqun Hu and Liwei Liu
Department of Mathematics, NanChang University,
Nanchang 330031, P.R. China
Department of Mathematics, Xi'an Jiaotong University,
Xi'an 710049, P.R.
China
Abstract:
By virtue of new analytic techniques, we analyze and
study
several strong convergence theorems for the approximation of
common fixed points of asymptotically demicontractive mappings
via the multistep iterative sequence with errors in Banach
spaces. Our results improve and extend the corresponding ones
announced by Osilike , Osilike and Aniagbosor, Igbokwe, Cho et
al., Moore and Nnoli, Hu and all the others.
Paper's Title:
Hyperbolic Models Arising in the Theory of Longitudinal Vibration of Elastic Bars
Author(s):
1I. Fedotov, 1J. Marais, 1,2M. Shatalov and 1H.M. Tenkam
1Department of Mathematics and Statistics,
Tshwane University
of
Technology
Private Bag X6680, Pretoria 0001
South Africa.
fedotovi@tut.ac.za,
julian.marais@gmail.com,
djouosseutenkamhm@tut.ac.za.
2Manufacturing and
Materials
Council of Scientific and Industrial
Research (CSIR)
P.O. Box 395, Pretoria, 0001
South Africa.
mshatlov@csir.co.za
Abstract:
In this paper a unified approach to the
derivation of families of one
dimensional hyperbolic differential equations and boundary conditions describing
the longitudinal vibration of elastic bars is outlined. The longitudinal and
lateral displacements are expressed in the form of a power series expansion in
the lateral coordinate. Equations of motion and boundary conditions are derived
using Hamilton's variational principle. Most of the well known models in this
field fall within the frames of the proposed theory, including the classical
model, and the more elaborated models proposed by by Rayleigh, Love, Bishop,
Mindlin, Herrmann and McNiven. The exact solution is presented for the
Mindlin-Herrmann case in terms of Green functions. Finally, deductions regarding
the accuracy of the models are made by comparison with the exact
Pochhammer-Chree solution for an isotropic cylinder.
Paper's Title:
Unital Compact Homomorphisms Between Extended Analytic Uniform Algebras
Author(s):
D. Alimohammadi and M. Mayghani
Department of Mathematics,
Faculty of Science, Arak University,
PO Box 38156-8-8349, Arak,
Iran.
Abstract:
Let X and K be compact plane sets with K⊆X. We denote by A(X,K) and A(X) the algebras of all continuous complex-valued functions on X which are analytic on int(K) and int(X), respectively. It is known that A(X,K) and A(X) are natural uniform algebras on X. A(X) and A(X,K) are called analytic uniform algebra and extended analytic uniform algebra on X, respectively. In this paper we study unital homomorphisms between extended analytic uniform algebras and investigate necessary and sufficient conditions for which these homomorphisms to be compact. We also determine the spectrum of unital compact endomorphisms of extended analytic uniform algebras.
Paper's Title:
A Dynamic Contact Problem for an Electro Viscoelastic Body
Author(s):
Denche M. and Ait Kaki L.
Laboratoire Equations Differentielles,
Departement de Mathematiques,
Universite Constantine 1,
Algeria.
Ecole Normale Superieure,
Departement des Sciences Exactes et Informatique,
Plateau Mansourah, Constantine.
Algeria.
E-mail:
m.denche@umc.edu.dz
leilaitkaki@yahoo.fr
Abstract:
We consider a dynamic problem which describes a contact between a piezoelectric body and a conductive foundation. The frictionless contact is modelled with the normal compliance, the electric conditions are supposed almost perfect. We prove the existence of a unique weak solution for almost perfect electric contact.
Paper's Title:
Kinematic Model for Magnetic Null-points in 2 Dimensions
Author(s):
Ali Khalaf Hussain Al-Hachami
Department of Mathematics,
College of Education For Pure Sciences,
Wasit University,
Iraq.
E-mail: alhachamia@uowasit.edu.iq
Abstract:
The adjacent configurations of two-dimensional magnetic null point centers are analyzed by an immediate examination about the null. The configurations are classified as either potential or non-potential. By then the non-potential cases are subdivided into three cases depending upon whether the component of current is less than, equal to or greater than a threshold current. In addition the essential structure of reconnection in 2D is examined. It unfolds that the manner by which the magnetic flux is rebuilt. In this paper, we center on the ramifications of kinematic arrangements; that is, we fathom just Maxwell's conditions and a resistive Ohm's law.
Paper's Title:
Numerical Approximation by the Method of Lines with Finite-volume Approach of a Solute Transport Equation in Periodic Heterogeneous Porous Medium
Author(s):
D. J. Bambi Pemba and B. Ondami
Université Marien Ngouabi,
Factuté des Sciences et Techniques,
BP 69, Brazzaville,
Congo.
E-mail: bondami@gmail.com
Abstract:
In this paper we are interested in the numerical approximation of a two-dimensional solute transport equation in heterogeneous porous media having periodic structures. It is a class of problems which has been the subject of various works in the literature, where different methods are proposed for the determination of the so-called homogenized problem. We are interested in this paper, in the direct resolution of the problem, and we use the method of lines with a finite volume approach to discretize this equation. This discretization leads to an ordinary differential equation (ODE) that we discretize by the Euler implicit scheme. Numerical experiments comparing the obtained solution and the homogenized problem solution are presented. They show that the precision and robustness of this method depend on the ratio between, the mesh size and the parameter involved in the periodic homogenization.
Paper's Title:
Generalized Composition Operators On Besov Spaces
Author(s):
Vishal Sharma, Sanjay Kumar and Stanzin Dolkar
Department of Mathematics,
Central University of Jammu,
Jammu and Kashmir,
India.
E-mail: sharmavishal911@gmail.com
Department of Mathematics,
Central University of Jammu,
Jammu and Kashmir,
India.
E-mail: sanjaykmath@gmail.com
Department of Mathematics,
Central University of Jammu,
Jammu and Kashmir,
India.
E-mail: stanzin.math@cujammu.ac.in
Abstract:
In this paper, we characterize boundedness, compactness and find the essential norm estimates for generalized composition operators between Besov spaces and Sp spaces.
Paper's Title:
Commutator For Singular Operators On Variable Exponent Sequence Spaces And Their Corresponding Ergodic Version
Author(s):
A.M. Alphonse and S.S.S. Anupindi
Department of Mathematics,
Birla Institute of Technology And Science- Pilani,
Hyderabad Campus, Jawahar Nagar, Kapra Mandal,
District.-Medchal-500 078, Telangana,
India.
E-mail:
alphonse@hyderabad.bits-pilani.ac.in
p20180442@hyderabad.bits-pilani.ac.in
URL:
https://www.bits-pilani.ac.in/hyderabad/a-michael-alphonse
https://www.bits-pilani.ac.in/research_scholars/sri-sakti-swarup-anupindi
Abstract:
In this paper, we prove strong type inequality for maximal commutator of singular operator on weighted lp spaces. Using these results we prove strong type inequality for the maximal commutator of singular operator on variable exponent sequence spaces. Using Calderon-Coifman-Weiss transference principle we prove strong type inequality for maximal ergodic commutator of singular operator on a probability space equipped with measure preserving transformation U.
Paper's Title:
Solving Strongly Nonlinear Fractional Fredholm Integral-Differential Equations in Caputo's Sense Using the SBA Method
Author(s):
Germain Kabore1, Bakari Abbo2, Ousseni So3 and Blaise Some1
1Laboratoire
d'Analyse Numerique, Informatique et de Biomathmathiques (L.N.I.BIO),
Universite Joseph Ki-Zerbo,
Burkina Faso.
E-mail: germainkabore982@gmail.com,
blaisesomeouaga1@gmail.com
2University
of N'Damena, Tchad.
E-mail: bakariabbo@yahoo.fr
3Laboratoire
d'Analyse Numerique, Informatique et de Biomathemathiques (L.N.I.BIO),
Ecole Normale Superieure,
Burkina Faso.
E-mail: sousseni@yahoo.fr
Abstract:
The work addressed in this article consists in constructing the exact solutions, where they exist, of fractional Fredholm-type integro-differential equations in the sense of Caputo. Our results are obtained using the SBA method. The simplification of the approach, the analysis of its convergence, and the generalization of this method to these types of highly nonlinear equations constitute our scientific contribution.
Paper's Title:
Positive Solutions of Evolution Operator Equations
Author(s):
Radu Precup
Department of Applied Mathematics,
Babes-Bolyai University,
Cluj, Romania
Abstract:
Existence and localization results are derived from Krasnoselskii’s compressionexpansion
fixed point theorem in cones, for operator equations in spaces of continuous functions
from a compact real interval to an abstract space. The main idea, first used in [12], is to handle
two equivalent operator forms of the equation, one of fixed point type giving the operator to
which Krasnoselskii’s theorem applies and an other one of coincidence type which is used to
localize a positive solution in a shell. An application is presented for a boundary value problem
associated to a fourth order partial differential equation on a rectangular domain.
Paper's Title:
Weak Solution for Hyperbolic Equations with a Non-Local Condition
Author(s):
Lazhar Bougoffa
King Khalid
University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics,
P.O.Box 9004, Abha, Saudi Arabia
abogafah@kku.edu.sa
Abstract:
In this paper, we study hyperbolic equations with a non-local condition. We prove
the existence and uniqueness of weak solutions, using energy inequality and the density of the
range of the operator generated by the problem.
Paper's Title:
An Easy and Efficient Way for Solving A class of Singular Two Point Boundary Value Problems
Author(s):
Muhammed I. Syam, Muhammed N. Anwar and Basem S. Attili
Mathematical Sciences Department
United Arab Emirates University, P. O. Box 17551
Al-Ain, United Arab Emirates
b.attili@uaeu.ac.ae
Abstract:
We will consider an efficient and easy way for solving a certain
class of singular two point boundary value problems. We will
employ the least squares method which proved to be efficient for
this type of problems. Enough examples that were considered by
others will be solved with comparison with the results presented
there.
Paper's Title:
A New Step Size Rule in Noor's Method for Solving General Variational Inequalities
Author(s):
Abdellah Bnouhachem
School of Management Science and Engineering, Nanjing University,
Nanjing, 210093
P.R. China.
babedallah@yahoo.com
Abstract:
In this paper, we propose a new step size rule in Noor's method
for solving general
variational inequalities. Under suitable conditions, we prove that the
new method is globally convergent. Preliminary numerical
experiments are included to illustrate the advantage and
efficiency of the proposed method.
Paper's Title:
Ergodic Solenoidal Homology II:
Density of Ergodic Solenoids
Author(s):
Vicente Muñoz and Ricardo Pérez Marco
Instituto de Ciencias Matem
áticas CSIC-UAM-UC3M-UCM,Abstract:
A measured solenoid is a laminated space endowed with a tranversal measure invariant by holonomy. A measured solenoid immersed in a smooth manifold produces a closed current (known as a generalized Ruelle-Sullivan current). Uniquely ergodic solenoids are those for which there is a unique (up to scalars) transversal measure. It is known that for any smooth manifold, any real homology class is represented by a uniquely ergodic solenoid. In this paper, we prove that the currents associated to uniquely ergodic solenoids are dense in the space of closed currents, therefore proving the abundance of such objects.
Paper's Title:
Some Open Problems in Analysis
Author(s):
A.G. Ramm
Mathematics Department, Kansas State University,
Manhattan, KS 66506-2602,
USA
ramm@math.ksu.edu
URL: http://www.math.ksu.edu/~ramm
Abstract:
In this paper some open problems in analysis are formulated. These problems were formulated and discussed by the author at ICMAA6.
Paper's Title:
Hyers-Ulam-Rassias Stability
of a Generalized Jensen Functional Equation
Author(s):
A. Charifi, B. Bouikhalene, E. Elqorachi and A. Redouani
Department of
Mathematics, Faculty of Sciences,
Ibn Tofail University,
Kenitra, Morocco
charifi2000@yahoo.fr
bbouikhalene@yahoo.fr
Department of
Mathematics, Faculty of Sciences,
Ibn Zohr University,
Agadir, Morocco
elqorachi@hotmail.com
Redouani-ahmed@yahoo.fr
Abstract:
In this paper we obtain the Hyers-Ulam-Rassias stability for the generalized Jensen's functional equation in abelian group (G,+). Furthermore we discuss the case where G is amenable and we give a note on the Hyers-Ulam-stability of the K-spherical (n × n)-matrix functional equation.
Paper's Title:
On some Strongly Nonlinear Elliptic Problems
in L¹-data with a Nonlinearity Having a Constant Sign in Orlicz
Spaces via Penalization Methods
Author(s):
E. Azroul, A. Benkirane and M. Rhoudaf
Dep. Math., Faculté des Sciences
Dhar-Mahraz,
B.P 1796 Atlas Fès,
Maroc
Departement of Mathematics,
Faculty of Sciences and Techniques of Tangier,
B.P. 416, Tangier,
Morocco.
rhoudaf_mohamed@yahoo.fr
Abstract:
This paper is concerned with the existence result of the
unilateral problem associated to the equations of the type
![]()
in Orlicz spaces, without
assuming the sign condition in the nonlinearity g. The source term f belongs to L¹(Ώ).
Paper's Title:
Shape Diagrams for 2D Compact Sets - Part III: Convexity
Discrimination for Analytic and Discretized Simply Connected Sets.
Author(s):
S. Rivollier, J. Debayle and J.-C. Pinoli
Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Mines de Saint-Etienne,
CIS - LPMG, UMR CNRS
5148,
158 cours Fauriel,
42023 Saint-Etienne Cedex 2, France.
rivollier@emse.fr;
debayle@emse.fr; pinoli@emse.fr
Abstract:
Shape diagrams are representations in the Euclidean plane introduced to study 3-dimensional and 2-dimensional compact convex sets. However, they can also been applied to more general compact sets than compact convex sets. A compact set is represented by a point within a shape diagram whose coordinates are morphometrical functionals defined as normalized ratios of geometrical functionals. Classically, the geometrical functionals are the area, the perimeter, the radii of the inscribed and circumscribed circles, and the minimum and maximum Feret diameters. They allow twenty-two shape diagrams to be built. Starting from these six classical geometrical functionals, a detailed comparative study has been performed in order to analyze the representation relevance and discrimination power of these twenty-two shape diagrams. The two first parts of this study are published in previous papers 8,9. They focus on analytic compact convex sets and analytic simply connected compact sets, respectively. The purpose of this paper is to present the third part, by focusing on the convexity discrimination for analytic and discretized simply connected compact sets..
Paper's Title:
A New Property of General Means of Order p with an Application to the Theory of Economic Growth
Author(s):
Olivier de La Grandville
Department of Management Science and Engineering,
Huang Engineering Center, Stanford University,
475 Via Ortega, Stanford, California 94305
U.S.A.
Abstract:
The purpose of this note is to demonstrate a new property of the
general mean of order p of m ordered positive numbers
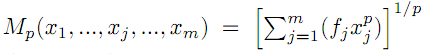
,
the elasticity of
with
respect to xm, defined by
,
tends towards zero, and therefore
.
This property is then applied to optimal growth theory.
Paper's Title:
Application of Equivalence Method to Classify Monge-Ampère Equations of Elliptic Type
Author(s):
Moheddine Imsatfia
E-mail: imsatfia@math.jussieu.fr
Abstract:
In this paper, we apply Cartan's equivalence method to give a local classification of Monge-Ampère equations of elliptic type. Then we find a necessary and sufficient conditions such that a Monge-Ampère equation is either contactomorphic to the Laplace equation or to an Euler-Lagrange equation.
Paper's Title:
On Eigenvalues and Boundary Curvature of the C*-algebra Numerical Rang
Author(s):
M. T. Heydari
Department of Mathematics,
College of Sciences,
Yasouj University,
Yasouj, 75914-74831,
Iran.
E-mail: heydari@yu.ac.ir
Abstract:
Let A be a C*-algebra with unit 1 and a∈A be a nilpotent. By Donoghue's Theorem, all corner points of its numerical range V(a) belong to the spectrum σ(a). It is therefore natural to expect that, more generally, the distance from a point p on the boundary ∂ V(a) of V(a) to σ(a) should be in some sense bounded by the radius of curvature of ∂ V(a) at p.
Paper's Title:
Credibility Based Fuzzy Entropy Measure
Author(s):
G. Yari, M. Rahimi, B. Moomivand and P. Kumar
Department of Mathematics,
Iran University
of Science and Technology,
Tehran,
Iran.
E-mail:
Yari@iust.ac.ir
E-mail:
Mt_Rahimi@iust.ac.ir
URL:
http://www.iust.ac.ir/find.php?item=30.11101.20484.en
URL:
http://webpages.iust.ac.ir/mt_rahimi/en.html
Qarzol-hasaneh
Mehr Iran Bank, Tehran,
Iran.
E-mail:
B.moomivand@qmb.ir
Department of Mathematics and Statistics,
University of Northern British Columbia,
Prince George, BC,
Canada.
E-mail:
Pranesh.Kumar@unbc.ca
Abstract:
Fuzzy entropy is the entropy of a fuzzy variable, loosely representing the information of uncertainty. This paper, first examines both previous membership and credibility based entropy measures in fuzzy environment, and then suggests an extended credibility based measure which satisfies mostly in Du Luca and Termini axioms. Furthermore, using credibility and the proposed measure, the relative entropy is defined to measure uncertainty between fuzzy numbers. Finally we provide some properties of this Credibility based fuzzy entropy measure and to clarify, give some examples.
Paper's Title:
Extreme Curvature of Polynomials and Level Sets
Author(s):
Stephanie P. Edwards, arah J. Jensen, Edward Niedermeyer, and Lindsay Willett
Department of Mathematics,
Hope College,
Holland, MI 49423,
U.S.A.
E-mail: sedwards@hope.edu
E-mail: tarahjaye@gmail.com
E-mail: eddie.niedermeyer@gmail.com
E-mail: willettlm1@gmail.com
WWW: http://math.hope.edu/sedwards/
Abstract:
Let f be a real polynomial of degree n. Determining the maximum number of zeros of kappa, the curvature of f, is an easy problem: since the zeros of kappa are the zeros of f'', the curvature of f is 0 at most n-2 times. A much more intriguing problem is to determine the maximum number of relative extreme values for the function kappa. Since kappa'=0 at each extreme point of kappa, we are interested in the maximum number of zeros of kappa'. In 2004, the first author and R. Gordon showed that if all the zeros of f'' are real, then f has at most n-1 points of extreme curvature. We use level curves and auxiliary functions to study the zeros of the derivatives of these functions. We provide a partial solution to this problem, showing that f has at most n-1 points of extreme curvature, given certain geometrical conditions. The conjecture that f has at most n-1 points of extreme curvature remains open.
Paper's Title:
Stability Analysis Epidemic Model of SIR Type (Susceptible, Infectious, Recovered) On The Spread Dynamic of Malaria in Ambon City
Author(s):
Alwi Smith
Education Faculty, Biology Education
Programme,
University of Pattimura,
Ir. M. Putuhena Street, Poka Ambon, Moluccas, 97233,
Indonesia.
E-mail: alwi.smith1963@gmail.com
Abstract:
This research discusses the spread of malaria in Ambon city through SIR (Susceptible, Infected, Recovered) model. This research analyzes the stability of equilibrium point on deterministic model and Basic Reproduction Ratio (R0). The result shows that the epidemic model has two equilibrium points. They are disease free equilibrium, [E0=[S,I,R]=[1,0,0]], and epidemic equilibrium, Ei=[S,I,R]= [5,497808;-3,680341;-0,818288]. The Basic Reproduction Ratio of malaria disease in Ambon city is 0,181891. This result implies that malaria disease in Ambon will not be an endemic, because malaria disease in Ambon city will be eradicated slowly over time.
Paper's Title:
The Influence of Fluid Pressure in Macromechanical Cochlear Model
Author(s):
F. E. Aboulkhouatem1, F. Kouilily1, N. Achtaich1, N. Yousfi1 and M. El Khasmi2
1Department
of Mathematics and Computer Science, Faculty of Sciences
Ben M'sik, Hassan II University, Casablanca,
Morocco.
2Department
of Biology, Faculty of Sciences
Ben M'sik, Hassan II University, Casablanca,
Morocco.
E-mail:
fatiaboulkhouatem@gemail.com
URL: http://www.fsb.univh2c.ma/
Abstract:
An increase of pressure in the structure of cochlea may cause a hearing loss. In this paper, we established the relationship between the fluid pressure and the amplitude of displacement of Basilar Membrane to clarify the mechanisms of hearing loss caused by increasing of this pressure. So, a mathematical cochlear model was formulated using finite difference method in order to explain and demonstrate this malfunction in passive model. Numerical simulations may be considered as helpful tools which may extend and complete the understanding of a cochlea dysfunction.
Paper's Title:
Some Convergence Results for Jungck-Am Iterative Process In Hyperbolic Spaces
Author(s):
Akindele Adebayo Mebawondu and Oluwatosin Temitope Mewomo
School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science,
University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban,
South Africa.
E-mail:
216028272@stu.ukzn.ac.za,
mewomoo@ukzn.ac.za
Abstract:
In this paper, we introduce a new three steps iterative process called Jungck-AM iterative process and show that the proposed iterative process can be used to approximate fixed points of Jungck-contractive type mappings and Jungck-Suzuki type mappings. In addition, we establish some strong and Δ-convergence results for the approximation of fixed points of Jungck-Suzuki type mappings in the frame work of uniformly convex hyperbolic space. Furthermore, we show that the newly proposed iterative process has a better rate of convergence compare to the Jungck-Noor, Jungck-SP, Jungck-CR and some existing iterative processes in the literature. Finally, stability, data dependency results for Jungck-AM iterative process is established and we present an analytical proof and numerical examples to validate our claim.
Paper's Title:
Action of Differential Operators On Chirpsconstruct On L∞
Author(s):
Taoufik El Bouayachi and Naji Yebari
Laboratoire de Mathematiques et
applications,
Faculty of sciences and techniques, Tangier,
Morocco.
E-mail:
figo407@gmail.com,
yebarinaji@gmail.com
Abstract:
We will study in this work the action of differential operators on L∞ chirps and we will give a new definition of logarithmic chirp. Finally we will study the action of singular integral operators on chirps by wavelet characterization and Kernel method.
Paper's Title:
The Concept of Convergence for 2-Dimensional Subspaces Sequence in Normed Spaces
Author(s):
M. Manuharawati, D. N. Yunianti, M. Jakfar
Mathematics Department, Universitas
Negeri Surabaya,
Jalan Ketintang Gedung C8,
Surabaya 60321,
Indonesia.
E-mail: manuharawati@unesa.ac.id,
dwiyunianti@unesa.ac.id,
muhammadjakfar@unesa.ac.id
Abstract:
In this paper, we present a concept of convergence of sequence, especially, of 2-dimensional subspaces of normed spaces. The properties of the concept are established. As consequences of our definition in an inner product space, we also obtain the continuity property of the angle between two 2-dimensional subspaces of inner product spaces.
Paper's Title:
Fractional exp(-φ(ξ))- Expansion Method and its Application to Space--Time Nonlinear Fractional Equations
Author(s):
A. A. Moussa and L. A. Alhakim
Department of Management Information
System and Production Management,
College of Business and Economics, Qassim University,
P.O. BOX 6666, Buraidah: 51452,
Saudi Arabia.
E-mail: Alaamath81@gmail.com
URL:
https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=ccztZdsAAAAJ&hl=ar
Department of Management Information
System and Production Management,
College of Business and Economics, Qassim University,
P.O. BOX 6666, Buraidah: 51452,
Saudi Arabia.
E-mail: Lama2736@gmail.com
URL:
https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=OSiSh1AAAAAJ&hl=ar
Abstract:
In this paper, we mainly suggest a new method that depends on the fractional derivative proposed by Katugampola for solving nonlinear fractional partial differential equations. Using this method, we obtained numerous useful and surprising solutions for the space--time fractional nonlinear Whitham--Broer--Kaup equations and space--time fractional generalized nonlinear Hirota--Satsuma coupled KdV equations. The solutions obtained varied between hyperbolic, trigonometric, and rational functions, and we hope those interested in the real-life applications of the previous two equations will find this approach useful.
Paper's Title:
Inequalities of Gamma Function Appearing in Generalizing Probability Sampling Design
Author(s):
Mohammadkheer M. Al-Jararha And Jehad M. Al-Jararha
Department of Mathematics,
Yarmouk University,
Irbid 21163,
Jordan.
E-mail: mohammad.ja@yu.edu.jo
Department of Statistics,
Yarmouk University,
Irbid 21163,
Jordan.
E-mail: jehad@yu.edu.jo
Abstract:
In this paper, we investigate the complete monotonicity of some functions involving gamma function. Using the monotonic properties of these functions, we derived some inequalities involving gamma and beta functions. Such inequalities can be used to generalize different probability distribution functions. Also, they can be used to generalize some statistical designs, e.g., the probability proportional to the size without replacement design.
Paper's Title:
Existence and Approximation of Traveling Wavefronts for the Diffusive Mackey-Glass Equation
Author(s):
C. Ramirez-Carrasco and J. Molina-Garay
Facultad de Ciencias Basicas,
Universidad Catolica del Maule, Talca,
Chile
E-mail: carloshrc1989@gmail.com
molina@imca.edu.pe
Abstract:
In this paper, we consider the diffusive Mackey-Glass model with discrete delay. This equation describes the dynamics of the blood cell production. We investigate the existence of traveling wavefronts solutions connecting the two steady states of the model. We develop an alternative proof of the existence of such solutions and we also demonstrate the existence of traveling wavefronts moving at minimum speed. The proposed approach is based on the use technique of upper-lower solutions. Finally, through an iterative procedure, we show numerical simulations that approximate the traveling wavefronts, thus confirming our theoretical results.
Paper's Title:
Sharp Inequalities Between Hölder and Stolarsky Means of Two Positive Numbers
Author(s):
M. Bustos Gonzalez and A. I. Stan
The University of Iowa,
Department of Mathematics,
14 MacLean Hall,
Iowa City, Iowa,
USA.
E-mail:
margarita-bustosgonzalez@uiowa.edu
The Ohio State University at Marion,
Department of Mathematics,
1465 Mount Vernon Avenue,
Marion, Ohio,
USA.
E-mail: stan.7@osu.edu
Abstract:
Given any index of the Stolarsky means, we find the greatest and least indexes of the H\"older means, such that for any two positive numbers, the Stolarsky mean with the given index is bounded from below and above by the Hölder means with those indexes, of the two positive numbers. Finally, we present a geometric application of this inequality involving the Fermat-Torricelli point of a triangle.
Paper's Title:
A New Method with Regularization for Solving Split Variational Inequality Problems in Real Hilbert Spaces
Author(s):
Francis Akutsah1 and Ojen Kumar Narain2
1School
of Mathematics,
Statistics and Computer Science,
University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban,
South Africa.
E-mail: 216040405@stu.ukzn.ac.za,
akutsah@gmail.com
2School
of Mathematics,
Statistics and Computer Science,
University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban,
South Africa.
E-mail: naraino@ukzn.ac.za
Abstract:
In this paper, we introduce a new inertial extrapolation method with regularization for approximating solutions of split variational inequality problems in the frame work of real Hilbert spaces. We prove that the proposed method converges strongly to a minimum-norm solution of the problem without using the conventional two cases approach. In addition, we present some numerical experiments to show the efficiency and applicability of the proposed method. The results obtained in this paper extend, generalize and improve several results in this direction.
Paper's Title:
Fekete-Szegö Inequality for Sakaguchi Type of functions in Petal Shaped Domain
Author(s):
E. K. Nithiyanandham and B. Srutha Keerthi
Division of Mathematics, School of
Advanced Sciences,
Vellore Institute of Technology Chennai Campus,
Chennai - 600 048,
India.
E-mail: nithiyankrish@gmail.com
Division of Mathematics, School of
Advanced Sciences,
Vellore Institute of Technology Chennai Campus,
Chennai - 600 048,
India.
E-mail: keerthivitmaths@gmail.com
Abstract:
In this paper, we estimate coefficient bounds,|a_2|,|a_3| and |a_4|, Fekete-Szegö inequality
![]() and Toeplitz determinant
T2(2) and T3(1) for functions belonging to the following class
and Toeplitz determinant
T2(2) and T3(1) for functions belonging to the following class

the function being holomorphic, we expand using Taylor series and obtain several corollaries and consequences for the main result.
Paper's Title:
Toeplitz Determinant for Sakaguchi Type Functions Under Petal Shaped Domain
Author(s):
B. Nandhini and B. Srutha Keerthi
Division of Mathematics, School of
Advanced Sciences,
Vellore Institute of Technology Chennai Campus,
Chennai - 600 048,
India.
E-mail:
nandhinibaskar1996@gmail.com
Division of Mathematics, School of
Advanced Sciences,
Vellore Institute of Technology Chennai Campus,
Chennai - 600 048,
India.
E-mail: keerthivitmaths@gmail.com
Abstract:
We introduce a new general subclass GPt,ρ of Sakaguchi kind function on a Petal shaped domain. We obtain coefficients bounds and upper bounds for the Fekete-Szegö functional over the class. From these functions we obtain the bounds of first four coefficients, and then we have derived the Toeplitz determinant T2(2) and T3(1) whose diagonal entries are the coefficients of functions.
Paper's Title:
New Refinements for Integral and Sum Forms of Generalized Hölder Inequality For N Term
Author(s):
M. Jakfar, Manuharawati, D. Savitri
Mathematics Department,
Universitas Negeri Surabaya
Jalan Ketintang Gedung C8, Surabaya, 60321
Indonesia.
E-mail: muhammadjakfar@unesa.ac.id
manuharawati@unesa.ac.id
diansavitri@unesa.ac.id
Abstract:
We know that in the field of functional analysis, Hölder inequality is very well known, important, and very applicable. So many researchers are interested in discussing these inequalities. Many world mathematicians try to improve these inequalities. In general, the Hölder inequality has two forms, namely the integral form and the sum form. In this paper, we will introduce a new refinement of the generalization of Hölder inequalities in both integral and addition forms. Especially in the sum form, improvements will be introduced that are better than the previous improvements that have been published by Jing-feng Tian, Ming-hu Ha, and Chao Wang.
Paper's Title:
Some Moduli and Inequalities Related to Birkhoff Orthogonality in Banach Spaces
Author(s):
Dandan Du and Yongjin Li
Department of Mathematics,
Sun Yat-sen University,
Guangzhou, 510275,
P.R. China.
E-mail: dudd5@mail2.sysu.edu.cn
Department of Mathematics,
Sun Yat-sen University,
Guangzhou, 510275,
P.R. China.
E-mail: stslyj@mail.sysu.edu.cn
Abstract:
In this paper, we shall consider two new constants δB(X) and ρB(X), which are the modulus of convexity and the modulus of smoothness related to Birkhoff orthogonality, respectively. The connections between these two constants and other well-known constants are established by some equalities and inequalities. Meanwhile, we obtain two characterizations of Hilbert spaces in terms of these two constants, study the relationships between the constants δB(X), ρB(X) and the fixed point property for nonexpansive mappings. Furthermore, we also give a characterization of the Radon plane with affine regular hexagonal unit sphere.
Paper's Title:
High Order Collocation Method for the Generalized Kuramoto-Sivashinsky Equation
Author(s):
Zanele Mkhize, Nabendra Parumasur and Pravin Singh
School of Mathematics, Statistics and
Computer Sciences,
University of KwaZulu-Natal,
Private Bag X 54001,
Durban 4000.
E-mail: mkhizez2@ukzn.ac.za
parumasurn1@ukzn.ac.za
singhp@ukzn.ac.za
URL: https://www.ukzn.ac.za
Abstract:
In this paper, we derive the heptic Hermite basis functions and use them as basis functions in the orthogonal collocation on finite elements (OCFE) method. We apply the method to solve the generalized Kuramoto-Sivashinsky equation. Various numerical simulations are presented to justify the computational efficiency of the proposed method.
Paper's Title:
On the Class of Totally Polynomially Posinormal Operators
Author(s):
E. Shine Lal, T. Prasad, P. Ramya
Department of Mathematics,University
College,
Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, 695034.
India.
E-mail: shinelal.e@gmail.com
Department of Mathematics,
University of Calicut,
Malapuram, Kerala 673635,
India.
E-mail: prasadvalapil@gmail.com
Department of Mathematics,
N.S.S College,
Nemmara, Kerala, 678508
India.
E-mail: ramyagcc@gmail.com
Abstract:
In this paper, we proved that if T ∈
B(H) is totally P-posinormal operator with
 . Moreover, we study spectral continuity and range kernel orthogonality of these class of operators.
. Moreover, we study spectral continuity and range kernel orthogonality of these class of operators.
Paper's Title:
Coefficient Bounds for Sakaguchi Kind of Functions Associated with Sine Function
Author(s):
Serap Bulut, H. Priya and B. Srutha Keerth
Kocaeli University,
Faculty of Aviation and Space Sciences,
Arslanbey Campus, 41285 Kartepe-Kocaeli,
Turkey.
E-mail: serap.bulut@kocaeli.edu.tr
Department of Mathematics,
School of Advanced Sciences,
VIT Chennai Campus, Chennai - 600 048,
India.
E-mail: priyaharikrishnan18@gmail.com,
priya.h2020@vitstudent.ac.in
Department of Mathematics,
School of Advanced Sciences,
VIT Chennai Campus, Chennai - 600 048,
India.
E-mail: keerthivitmaths@gmail.com,
sruthakeerthi.b@vit.ac.in
Abstract:
In this paper, we introduce a new general subclass of analytic functions with respect to symmetric points in the domain of sine function. We obtain sharp coefficient bounds and upper bounds for the Fekete-Szegö functional. Also we get sharp bounds for the logarithmic coefficients of functions belonging to this new class.
Paper's Title:
Jordan Canonical Form of Interval Matrices and Applications
Author(s):
S. Hema Surya, T. Nirmala and K. Ganesan
Department of Mathematics, College of
Engineering and Technology,
SRM Institute of Science and Technology,
Kattankulathur,
Chennai-603203,
India.
E-mail: nirmalat@srmist.edu.in
URL:
https://www.srmist.edu.in/faculty/dr-t-nirmala/
Abstract:
A square interval matrix over R can be converted to diagonal form if certain prerequisites are satisfied. However not all square matrices can be diagonalized. As a consequence, we strive the next simplest form to which it can be reduced while retaining important properties such as eigenvalues, rank, nullity, and so on. It turns out that any real interval matrix has a Jordan Canonical Form (JCF) over E if it has n interval eigenvalues in IR. We discuss in this paper a method for computing the Jordan canonical form of an interval matrix using a new pairing technique and a new type of interval arithmetic that will make classifying and analyzing interval matrices easier and more efficient. We conclude with a numerical example that supports the theory and application of predator-prey model.
Paper's Title:
On the Oscillatory Behavior of Self Adjoint Fractional Extensible Beam Equations
Author(s):
S. Priyadharshini1, G.E. Chatzarakis2, S. L. Panetsos2 and V. Sadhasivam1
1Post
Graduate and Research Department of Mathematics,
Thiruvalluvar Government Arts College,
Rasipuram - 637 401, Namakkal Dt., Tamil Nadu,
India.
E-mail: s.priya25april@gmail.com,
ovsadha@gmail.com
2Department
of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Educators,
School of Pedagogical and Technological Education(ASPETE),
Marousi 15122, Athens,
Greece.
E-mail: geaxatz@otenet.gr,
gea.xatz@aspete.gr,
spanetsos@aspete.gr
Abstract:
The main objective of this paper is to study the oscillatory behavior of the solutions of self adjoint fractional extensible beam equations by using integral average method. Some new sufficient conditions are established with various boundary conditions over a cylindrical domains. Examples illustrating the results are given.
Search and serve lasted 0 second(s).